Swollen glands
Swollen glands (also called swollen lymph nodes) are very common in young children, especially under the age of 5. They are usually a normal response to childhood infections such as colds or tonsillitis.
Lymph nodes are part of our immune system. The picture below shows how lymph nodes (glands) are connected by the lymphatic system throughout your child's body.
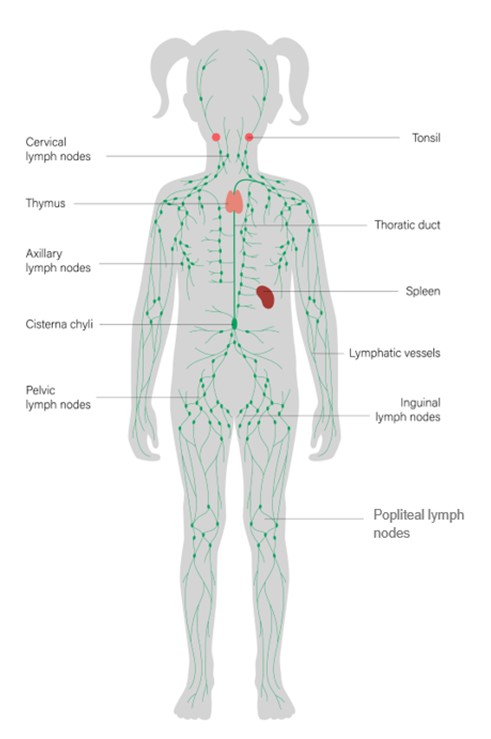
It is normal for lymph nodes to swell near the site of an infection. Neck (cervical) lymph nodes are the most likely to be affected. If your child has a sore throat then you might notice they have swollen glands in their neck.
Lymph nodes less than 2 centimetres in diameter are unlikely to indicate anything serious. Antibiotics are not normally needed.
Children with eczema sometimes have swollen lymph nodes. They will improve with treatment of your child’s eczema.
When should I worry?
If your child has any of the following:
- A temperature less than 36oC or temperature 38oC or more if baby is less than 3 months
- Breathing very fast, or breathing that stops or pauses
- Working hard to breathe, drawing in of the muscles below the rib, unable to talk or noisy breathing (grunting)
- Becomes pale, blue, mottled or unusually cold to touch
- Difficult to wake up, very sleepy or confused
- Has a fit (seizure)
- Develops a rash that does not disappear with pressure and seems unwell (see the 'Glass Test')
You need urgent help.
Go to the nearest Hospital Emergency (A&E) Department or phone 999
If your child has any of the following:
- Continues to have a fever of 38.0°C or above for more than 5 days
- Develops pain and redness of the lymph node
- A lymph node that is getting bigger quickly
- Big lymph nodes, more than 2 centimetres, for more than 6 weeks
- Unexplained bruising
- Weight loss
- Night sweats (where your child’s bedding is soaked through in the morning meaning that you need to change the sheets)
- Swollen glands in lots of different areas of the body
- Leg pains or limp
- If prescribed antibiotics and the fever has continued for more than 2 days or the gland has not got smaller after 5 days
- Household contact with TB
You need to contact a doctor or nurse today.
Please ring your GP surgery or call NHS 111
If your child has none of the above
Small lymph nodes (less than 1cm) are normal
Watch them closely for any change and look out for any red or amber symptoms
Self care
Continue providing your child’s care at home. If you are still concerned about your child, call NHS 111
This guidance has been reviewed and adapted by healthcare professionals across West Yorkshire with consent from the Hampshire development groups.
What should you look out for?
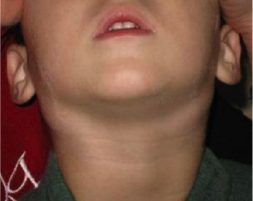 Painless big lymph nodes on both sides of the neck (bilateral) with a sore throat are likely to improve without antibiotics.
Painless big lymph nodes on both sides of the neck (bilateral) with a sore throat are likely to improve without antibiotics.
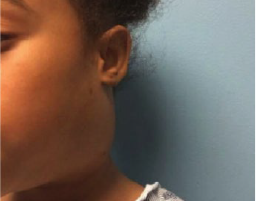 Sometimes a large, hot, painful, swollen lymph node may be due to a bacterial infection (bacterial lymphadenitis). This will need antibiotics.
Sometimes a large, hot, painful, swollen lymph node may be due to a bacterial infection (bacterial lymphadenitis). This will need antibiotics.
Very rarely, swollen glands may be a sign of less common infections (like TB) or cancer.
How can I help my child?
Use painkillers such as ibuprofen and paracetamol to keep your child comfortable. Please read and follow the instructions on the medicine packet.
When will it get better?
Small nodes in the neck, that can be moved under the skin are simply normal nodes.
Your child should start getting better within a couple of days but their lymph nodes may take 2 to 4 weeks to improve. Small lymph nodes (less than 1 cm) are normal.
Small lymph nodes that are less than 2 centimetres, particularly in the neck, that persist or change in size (sometimes smaller, sometimes bigger) are rarely of any concern and do not usually need further investigation.
Lymph nodes that continue to measure more than 2 centimetres for longer than 6 weeks need further investigation by a specialist doctor. Most of these lymph nodes are likely to be normal.
You can treat your child's very minor illnesses and injuries at home.
Some illnesses can be treated in your own home with support and advice from the services listed when required, using the recommended medicines and getting plenty of rest.
Sound advice
Children can recover from illness quickly but also can become more poorly quickly; it is important to seek further advice if a child's condition gets worse.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
You can treat your child's very minor illnesses and injuries at home.
Some illnesses can be treated in your own home with support and advice from the services listed when required, using the recommended medicines and getting plenty of rest.
Sound advice
Children can recover from illness quickly but also can become more poorly quickly; it is important to seek further advice if a child's condition gets worse.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
All community pharmacies across England are required to be Healthy Living Pharmacies. This means that they are able to offer advice on a range of healthy living matters which includes eating a healthy diet. They can provide information leaflets and give parents, carers and young people more information about other organisations that might also be able to help.
Pharmacists are experts in many aspects of healthcare, and can offer advice on a wide range of long-term conditions and common illnesses such as coughs, colds and stomach upsets. You don’t need an appointment, and many have private consultation areas. Your pharmacist will say if you need further medical attention.
Sound advice
- Visit a pharmacy if your child is ill, but does not need to see a GP.
- Remember that if your child's condition gets worse, you should seek further medical advice immediately.
- Help your child to understand. Watch this video with them about going to the pharmacy.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
All community pharmacies across England are required to be Healthy Living Pharmacies. This means that they are able to offer advice on a range of healthy living matters which includes eating a healthy diet. They can provide information leaflets and give parents, carers and young people more information about other organisations that might also be able to help.
Pharmacists are experts in many aspects of healthcare, and can offer advice on a wide range of long-term conditions and common illnesses such as coughs, colds and stomach upsets. You don’t need an appointment, and many have private consultation areas. Your pharmacist will say if you need further medical attention.
Sound advice
- Visit a pharmacy if your child is ill, but does not need to see a GP.
- Remember that if your child's condition gets worse, you should seek further medical advice immediately.
- Help your child to understand. Watch this video with them about going to the pharmacy.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
Health visitors are nurses or midwives who are passionate about promoting healthy lifestyles and preventing illness through the delivery of the Healthy Child Programme. They work with you through your pregnancy up until your child is ready to start school.
Health Visitors can also make referrals for you to other health professionals for example hearing or vision concerns, or to the Community Paediatricians, or the child and adolescent mental health services.
Contact your local Health Visiting Team:
Bradford Health Visitors or call - 01274 221223
Wakefield Health Visitors or call - 0300 373 0944
Craven Health Visitors or call - 01423 544265
Leeds Health Visitors or call - 0113 843 5683
Calderdale Health Visitors or call - 030 0304 5555 (local rate number)
Kirklees Health Visitors or call - 030 0304 5555 (local rate number)
Sound advice
Health visitors also provide advice, support and guidance in caring for your child, including:
- Breastfeeding, weaning and healthy eating
- Exercise, hygiene and safety
- Your child’s growth and development
- Emotional health and wellbeing, including postnatal depression
- Safety in the home
- Stopping smoking
- Contraception and sexual health
- Sleep and behaviour management (including temper tantrums!)
- Toilet training
- Minor illnesses
For more information about what Health Visitors do: What does a health visitor do?
Health visitors are nurses or midwives who are passionate about promoting healthy lifestyles and preventing illness through the delivery of the Healthy Child Programme. They work with you through your pregnancy up until your child is ready to start school.
Health Visitors can also make referrals for you to other health professionals for example hearing or vision concerns, or to the Community Paediatricians, or the child and adolescent mental health services.
Contact your local Health Visiting Team:
Bradford Health Visitors or call - 01274 221223
Wakefield Health Visitors or call - 0300 373 0944
Craven Health Visitors or call - 01423 544265
Leeds Health Visitors or call - 0113 843 5683
Calderdale Health Visitors or call - 030 0304 5555 (local rate number)
Kirklees Health Visitors or call - 030 0304 5555 (local rate number)
Sound advice
Health visitors also provide advice, support and guidance in caring for your child, including:
- Breastfeeding, weaning and healthy eating
- Exercise, hygiene and safety
- Your child’s growth and development
- Emotional health and wellbeing, including postnatal depression
- Safety in the home
- Stopping smoking
- Contraception and sexual health
- Sleep and behaviour management (including temper tantrums!)
- Toilet training
- Minor illnesses
For more information about what Health Visitors do: What does a health visitor do?
School nurses care for children and young people, aged 5 to19, and their families, to ensure their health needs are supported within their school and community. They work closely with education staff and other agencies to support parents, carers and the children and young people, with physical and, or emotional health needs.
Contacting the School Nurse
Primary and secondary schools have an allocated school nurse. Phone your child’s school to ask for the contact details of your named school nurse.
There is also a specialist nurse who works with families who choose to educate their children at home.
Contact your local school nursing team:
Bradford School Nurses 01274 221203
Wakefield School Nurses (0 to 19 service) 0300 373 0944 (local rate number)
Leeds School Nurses 0113 843 5683
Calderdale School Nurses 030 3330 9974 (local rate number)
Kirklees School Nurses 0300 304 5555 (local rate number)
Sound Advice
Before your child starts school your health visitor will meet with the school nursing team to transfer their care to the school nursing service. The school nursing team consists of a school nursing lead, specialist public health practitioners and school health staff nurses.
They all have a role in preventing disease and promoting health and wellbeing, by:
- encouraging healthier lifestyles
- offering immunisations
- giving information, advice and support to children, young people and their families
- supporting children with complex health needs
Each member of the team has links with many other professionals who also work with children including community paediatricians, child and adolescent mental health teams, health visitors and speech and language therapists. The school health nursing service also forms part of the multi-agency services for children, young people and families where there are child protection or safeguarding issues.
School nurses care for children and young people, aged 5 to19, and their families, to ensure their health needs are supported within their school and community. They work closely with education staff and other agencies to support parents, carers and the children and young people, with physical and, or emotional health needs.
Contacting the School Nurse
Primary and secondary schools have an allocated school nurse. Phone your child’s school to ask for the contact details of your named school nurse.
There is also a specialist nurse who works with families who choose to educate their children at home.
Contact your local school nursing team:
Bradford School Nurses 01274 221203
Wakefield School Nurses (0 to 19 service) 0300 373 0944 (local rate number)
Leeds School Nurses 0113 843 5683
Calderdale School Nurses 030 3330 9974 (local rate number)
Kirklees School Nurses 0300 304 5555 (local rate number)
Sound Advice
Before your child starts school your health visitor will meet with the school nursing team to transfer their care to the school nursing service. The school nursing team consists of a school nursing lead, specialist public health practitioners and school health staff nurses.
They all have a role in preventing disease and promoting health and wellbeing, by:
- encouraging healthier lifestyles
- offering immunisations
- giving information, advice and support to children, young people and their families
- supporting children with complex health needs
Each member of the team has links with many other professionals who also work with children including community paediatricians, child and adolescent mental health teams, health visitors and speech and language therapists. The school health nursing service also forms part of the multi-agency services for children, young people and families where there are child protection or safeguarding issues.
GPs assess, treat and manage a whole range of health problems. They also provide health education, give vaccinations and carry out simple surgical procedures. Your GP will arrange a referral to a hospital specialist should you need it.
All children should be registered with a GP. Anyone in England can register for free with a GP surgery. You do not need proof of address or immigration status, ID or an NHS number.
Sound advice
You have a choice of service:
- Doctors/GPs can treat many illnesses that do not warrant a visit to A&E.
- Help your child to understand. Watch this video with them about visiting the GP or going to a walk in centre
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
GPs assess, treat and manage a whole range of health problems. They also provide health education, give vaccinations and carry out simple surgical procedures. Your GP will arrange a referral to a hospital specialist should you need it.
All children should be registered with a GP. Anyone in England can register for free with a GP surgery. You do not need proof of address or immigration status, ID or an NHS number.
Sound advice
You have a choice of service:
- Doctors/GPs can treat many illnesses that do not warrant a visit to A&E.
- Help your child to understand. Watch this video with them about visiting the GP or going to a walk in centre
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
If you’re not sure which NHS service you need, call 111. An adviser will ask you questions to assess your symptoms and then give you the advice you need, or direct you straightaway to the best service for you in your area.
Please note, the online version of NHS 111 is only recommended for children over the age of 5. If your child is under 5 years old, please phone 111.
NHS 111 can also direct you to your nearest urgent treatment centre (minor injuries unit or walk-in centre).
Sound advice
Use NHS 111 if you are unsure what to do next, have any questions about a condition or treatment or require information about local health services.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
If you’re not sure which NHS service you need, call 111. An adviser will ask you questions to assess your symptoms and then give you the advice you need, or direct you straightaway to the best service for you in your area.
Please note, the online version of NHS 111 is only recommended for children over the age of 5. If your child is under 5 years old, please phone 111.
NHS 111 can also direct you to your nearest urgent treatment centre (minor injuries unit or walk-in centre).
Sound advice
Use NHS 111 if you are unsure what to do next, have any questions about a condition or treatment or require information about local health services.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
A&E departments provide vital care for life-threatening emergencies, such as:
- loss of consciousness
- breathing difficulties
- severe bleeding that cannot be stopped
- major trauma such as road traffic collisions
If you’re not sure it’s an emergency, call 111 for advice.
Sound advice
A&E departments provide vital care for life-threatening emergencies, such as:
- loss of consciousness
- breathing difficulties
- severe bleeding that cannot be stopped
- major trauma such as road traffic collisions
If you’re not sure it’s an emergency, call 111 for advice.



